Understanding Modern Nitrogen Supply Solutions
The choice between nitrogen generators and liquid nitrogen represents a critical decision for industries requiring consistent nitrogen supply. As manufacturing processes become increasingly sophisticated, businesses must carefully evaluate their nitrogen generation options to optimize operational costs while maintaining production quality. This comprehensive analysis explores the economic implications, practical considerations, and long-term impact of choosing between nitrogen generators and liquid nitrogen systems.
Financial Analysis of Nitrogen Supply Methods
Initial Investment Considerations
When evaluating nitrogen generators against liquid nitrogen solutions, the upfront investment demands careful consideration. Nitrogen generators typically require a more substantial initial capital outlay, including equipment costs, installation fees, and facility modifications. A standard nitrogen generator system may range from $50,000 to $200,000, depending on capacity requirements and specifications.
Conversely, liquid nitrogen setup costs appear more modest at first glance. Initial expenses primarily involve storage tank installation and basic pipeline infrastructure, often ranging from $10,000 to $30,000. However, this lower barrier to entry must be weighed against long-term operational expenses.
Operational Cost Analysis
The operational costs of nitrogen generators primarily consist of electricity consumption and routine maintenance. Modern nitrogen generators typically consume 0.3-0.5 kWh per cubic meter of nitrogen produced. Annual maintenance costs usually represent about 2-5% of the initial investment, covering filter replacements, component inspections, and occasional repairs.
Liquid nitrogen costs, however, are ongoing and subject to market fluctuations. Current prices range from $0.35 to $1.50 per hundred cubic feet, not including delivery charges, boil-off losses, and handling expenses. These recurring costs can accumulate significantly over time, particularly for high-volume users.
Operational Efficiency and Production Control
Supply Chain Independence
Nitrogen generators offer remarkable autonomy in gas production. Once installed, these systems provide a continuous, reliable nitrogen supply without dependence on external vendors. This self-sufficiency eliminates concerns about delivery schedules, supply chain disruptions, or emergency shortages that can impact production schedules.
The independence gained through nitrogen generators becomes particularly valuable during peak production periods or unexpected demand surges. Organizations can adjust their nitrogen production levels instantly without coordinating with suppliers or waiting for delivery slots.
Quality and Purity Management
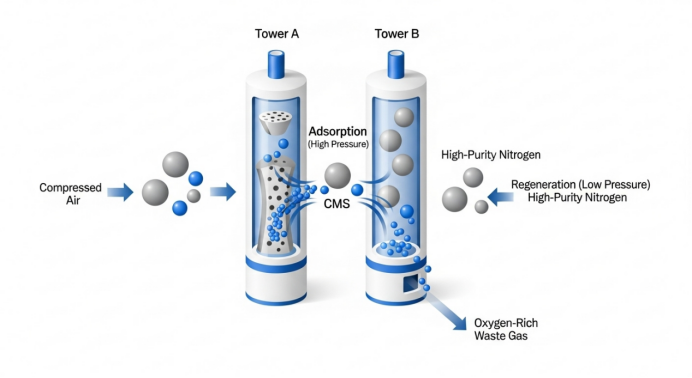
Modern nitrogen generators consistently deliver precise purity levels, typically ranging from 95% to 99.999%, depending on the application requirements. This controlled production ensures stable quality parameters crucial for sensitive manufacturing processes.
While liquid nitrogen generally offers high purity levels, maintaining this quality through storage and transfer processes requires careful handling. Evaporation losses and potential contamination during transfers can affect both quality and cost efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Carbon Footprint Analysis
The environmental impact of nitrogen supply methods has become increasingly important in corporate decision-making. Nitrogen generators typically demonstrate superior environmental performance due to their localized production model. By eliminating regular delivery requirements, they significantly reduce transportation-related carbon emissions.
Studies suggest that switching from liquid nitrogen delivery to on-site generation can reduce transportation-related carbon emissions by up to 90%. This reduction becomes particularly significant for facilities with high nitrogen consumption rates requiring frequent deliveries.
Resource Conservation
Nitrogen generators operate on a demand-based system, producing nitrogen only when needed. This efficient approach minimizes waste and energy consumption compared to liquid nitrogen systems, where boil-off losses can range from 0.3% to 1% per day, even with modern storage technologies.
Additionally, the elimination of disposable storage containers and reduced packaging waste contributes to improved environmental sustainability. Many organizations find these environmental benefits align well with their corporate sustainability goals and regulatory compliance requirements.
Long-term Strategic Benefits
Scalability and Future Growth
Nitrogen generators offer excellent scalability options for growing operations. Systems can be designed with expansion capabilities, allowing businesses to increase production capacity without completely replacing existing infrastructure. This flexibility proves valuable as operations evolve and nitrogen demands change.
The modular nature of many nitrogen generator systems enables phased implementation, allowing organizations to match their investment with current needs while maintaining the ability to scale up efficiently when required.
Risk Management and Control
On-site nitrogen generation significantly reduces supply chain risks associated with external dependencies. This control becomes particularly valuable during market disruptions, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events that might affect liquid nitrogen availability or pricing.
The predictable cost structure of nitrogen generators also helps in long-term financial planning, eliminating exposure to market price volatility common with liquid nitrogen supplies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical payback period for nitrogen generators?
The payback period for nitrogen generators typically ranges from 12 to 24 months, depending on current liquid nitrogen costs, consumption volumes, and specific operational requirements. Facilities with high nitrogen usage often experience faster return on investment due to greater cost savings.
How does maintenance compare between the two systems?
Nitrogen generators require regular scheduled maintenance, including filter changes and system checks, typically performed quarterly or bi-annually. Liquid nitrogen systems need less frequent maintenance but require constant monitoring of storage conditions and regular safety inspections for delivery infrastructure.
What factors most influence the choice between nitrogen generators and liquid nitrogen?
Key decision factors include monthly nitrogen consumption volume, required purity levels, available space for equipment installation, initial budget constraints, and long-term operational strategy. Organizations must also consider their technical expertise, maintenance capabilities, and growth projections when making this choice.